Sumer (from Akkadian Šumeru; Sumerian ki-en-ĝir15, approximately "land of the civilized lords" or "native land") was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age. Although the earliest historical records in the region do not go back much further than ca. 2900 BC, modern historians have asserted that Sumer was first settled between ca. 4500 and 4000 BC by a non-Semitic people who possibly did not speak the Sumerian language (pointing to the names of cities, rivers, basic occupations, etc. as evidence). These conjectured, prehistoric people are now called "proto-Euphrateans" or " Ubaidians", and are theorized to have evolved from the Samarra culture of northern Mesopotamia. The Ubaidians were the first civilizing force in Sumer, draining the marshes for agriculture, developing trade, and establishing industries, including weaving, leatherwork, metalwork, masonry, and pottery. However, some, such as Piotr Michalowski and Gerd Steiner, contest the idea of a Proto-Euphratean language or one substrate language.
Extreme weather in China
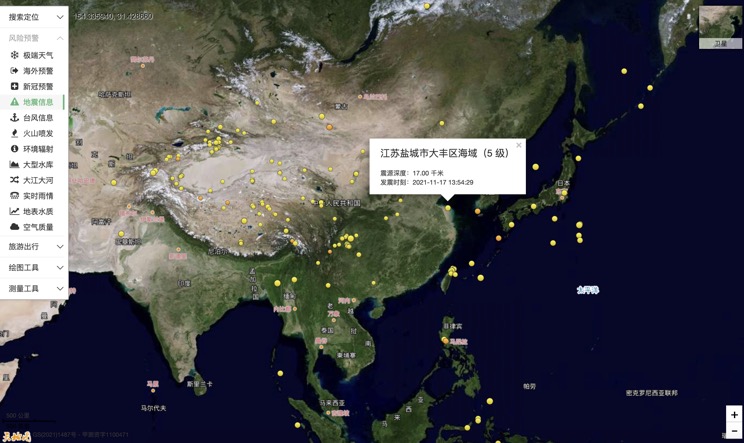
China Earthquake Information
Volcano eruption
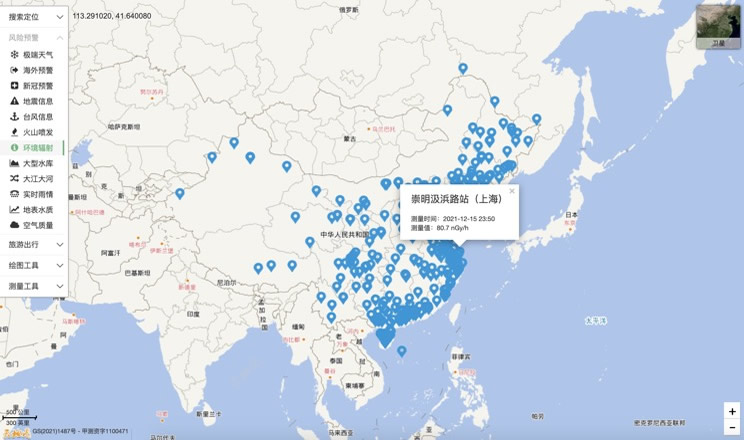
Environmental Radiation in China
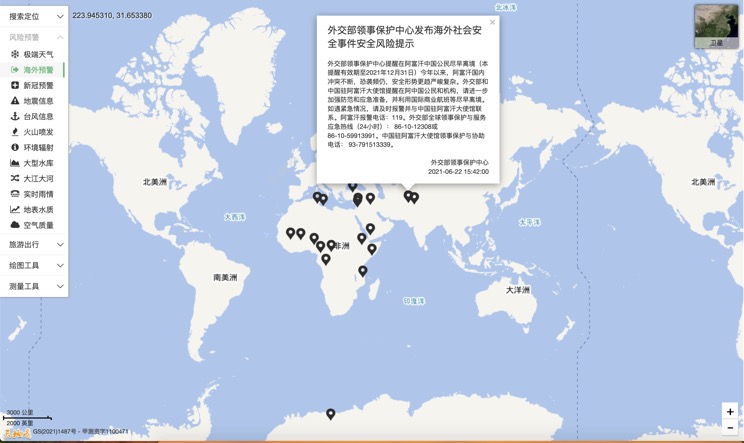
Overseas Warning
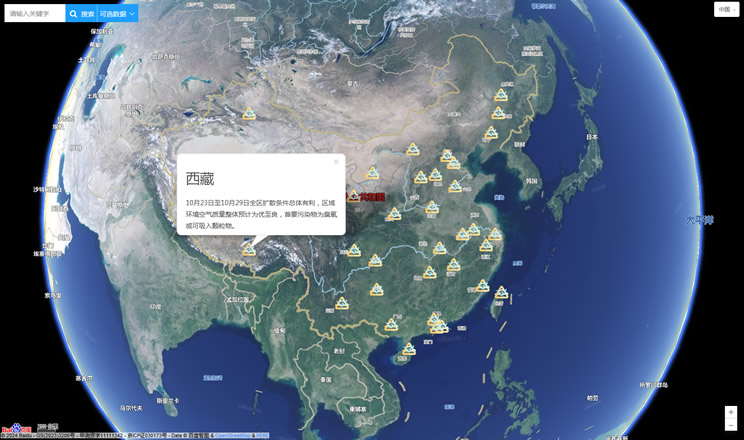
China's air quality
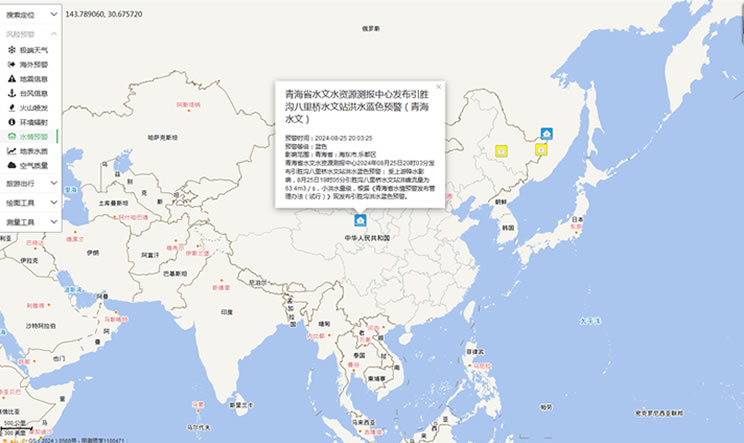
China's Water Disaster Alert
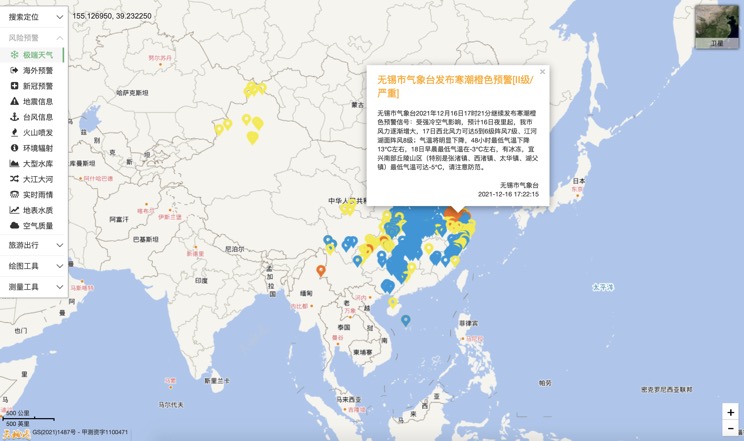
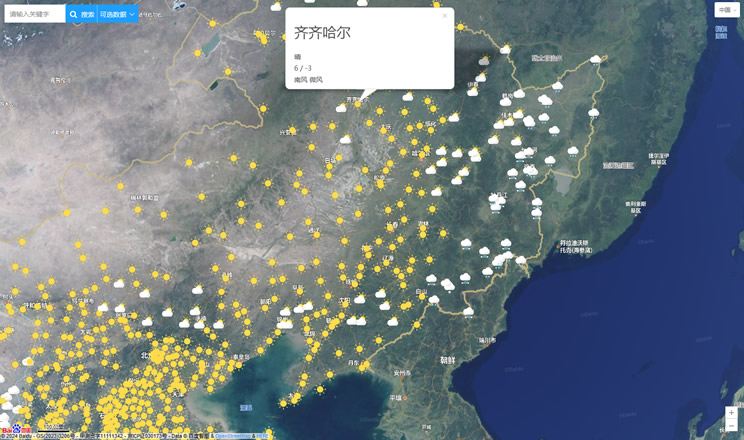
China Weather Forecast
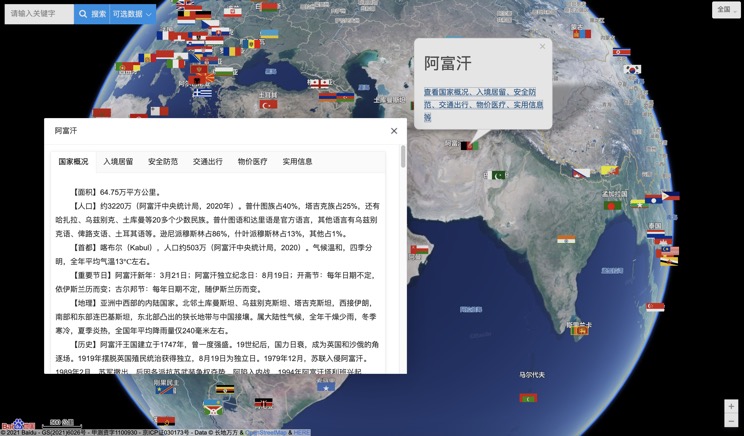
Introduction to Countries
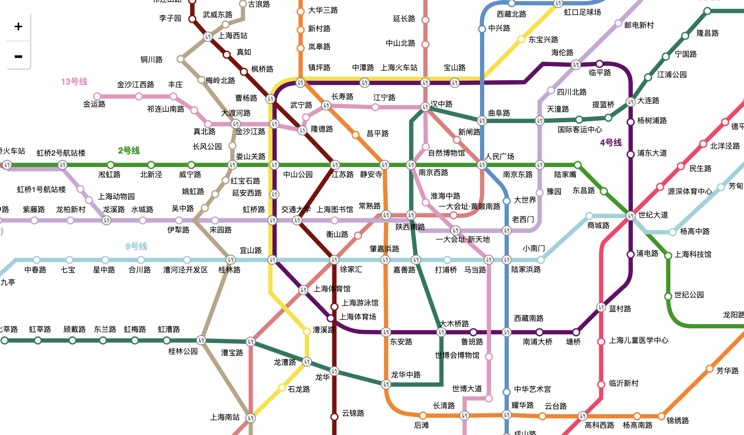
China Subway Lines
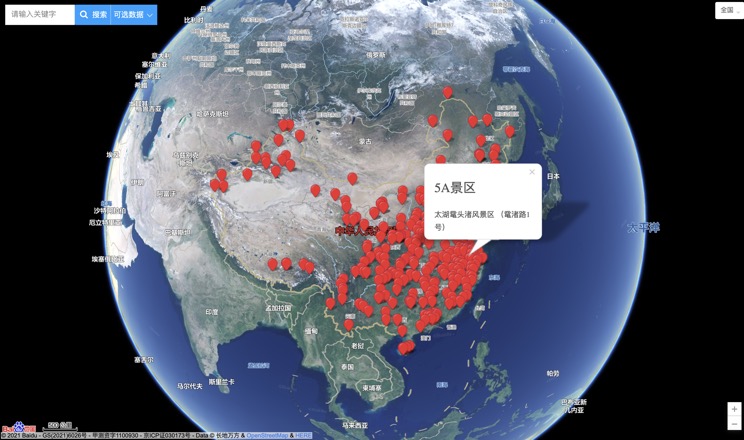
China's 5A Scenic Spots
Provincial Capitals in China